What are the Symptoms of Prostate Cancer, How to Spot and Treat the Disease
Prostate cancer is a prevalent form of cancer that affects the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped organ in the male reproductive system. It develops when abnormal cells in the prostate gland grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that can interfere with normal urinary and sexual functions.
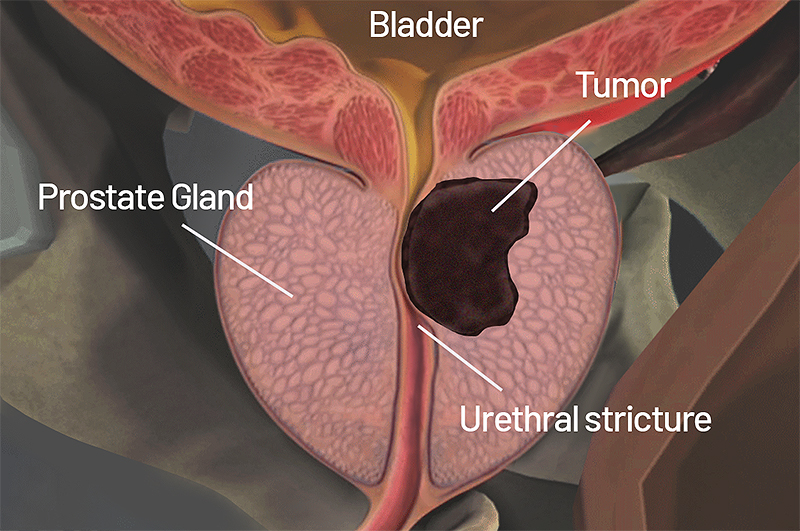
Prostate cancer is a significant health concern for men, but early detection and appropriate treatment can lead to favorable outcomes. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of prostate cancer, including its causes, risk factors, symptoms, and various treatment options available to patients.
- Prostate Cancer: Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention: The exact cause of prostate cancer remains unknown, but certain risk factors can increase an individual’s likelihood of developing the disease. These factors include age (risk increases with age, particularly after 50), family history of prostate cancer, race (African-American men have a higher risk), and certain genetic mutations. While it is not always possible to prevent prostate cancer, adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a balanced diet, and regular medical check-ups can contribute to early detection and improved treatment outcomes.
- Symptoms and Diagnosis: In the early stages, prostate cancer often shows no noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, common signs may include urinary difficulties (frequent urination, weak urine flow, blood in the urine), erectile dysfunction, pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, and bone pain. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood tests, digital rectal examinations (DRE), and imaging tests (such as MRI or ultrasound) are used to diagnose prostate cancer and determine its stage and aggressiveness.
- Treatment Options: The treatment plan for prostate cancer depends on several factors, including the cancer stage, the aggressiveness of the tumor, the patient’s age, overall health, and personal preferences. The primary treatment modalities include:
a) Active Surveillance: For slow-growing and low-risk prostate cancer, active surveillance may be recommended. Regular monitoring of the cancer’s progression is carried out, and treatment is initiated only if there are signs of tumor growth.
b) Surgery: Surgical intervention, known as a radical prostatectomy, involves the removal of the prostate gland and surrounding tissues. It can be performed through traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery.
c) Radiation Therapy: High-energy radiation is used to kill cancer cells or inhibit their growth. External beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy (internal radiation) are two common types of radiation therapy used in prostate cancer treatment.
d) Hormone Therapy: Prostate cancer cells often rely on male hormones (such as testosterone) for growth. Hormone therapy aims to block or suppress the effects of these hormones, either through medication or surgical removal of the testicles.
e) Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It may be recommended for advanced-stage prostate cancer or when other treatment options have not been effective.
f) Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy drugs stimulate the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. This treatment option is still under investigation for prostate cancer but shows promising results in certain cases.
- Lifestyle Modifications and Supportive Care: Alongside the primary treatment approaches, lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing stress can contribute to overall well-being and treatment outcomes. Supportive care, including pain management, counseling, and support groups, plays a crucial role in addressing the physical and emotional needs of individuals with prostate cancer.
Conclusion: Prostate cancer is a significant health concern for men, but advancements in diagnosis and treatment have improved patient outcomes. Regular screenings, awareness of risk factors, and proactive health management are vital for early./ albeu
Prostate Cancer Symptoms Treat Prostate Cancer Symptoms Treat