Thyroid Cancer : Types , Symptoms , Diagnosis , and Treatment Options
Thyroid cancer is a relatively rare but significant form of cancer that affects the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck.
It develops when abnormal cells in the thyroid gland grow and divide uncontrollably, forming a tumor. Thyroid cancer is highly treatable, especially when diagnosed at an early stage. In this article, we will delve into the details of thyroid cancer, including its types, symptoms, methods of diagnosis, and various treatment options available to patients.
- Understanding Thyroid Cancer: Thyroid cancer can be categorized into different types, including papillary carcinoma, follicular carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, and anaplastic carcinoma. Papillary carcinoma is the most common type and tends to grow slowly, while anaplastic carcinoma is rare but more aggressive. Medullary carcinoma originates from the C cells in the thyroid gland, and follicular carcinoma arises from the follicular cells. Each type has unique characteristics and requires specific treatment approaches.
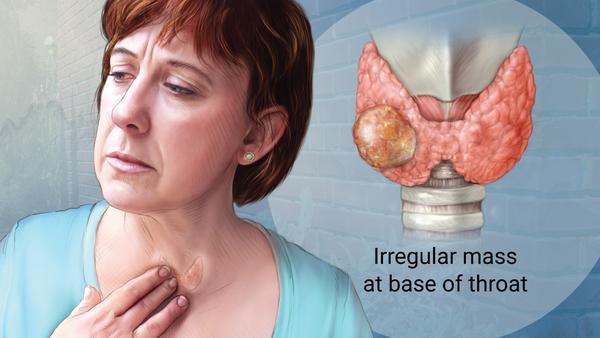
- Symptoms and Risk Factors: In the early stages, thyroid cancer may not exhibit noticeable symptoms. However, as the tumor grows, individuals may experience symptoms such as a lump or nodule in the neck, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes, and changes in voice. Risk factors for thyroid cancer include a family history of the disease, exposure to radiation, certain genetic syndromes, and being female.
- Diagnosis and Staging: Thyroid cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI), and biopsy of the thyroid tissue to confirm the presence of cancerous cells. Staging is an important aspect of diagnosis and involves determining the extent of the cancer’s spread within the thyroid gland and to nearby lymph nodes or other organs. Staging helps guide treatment decisions.
- Treatment Options: The treatment of thyroid cancer depends on several factors, including the type, stage, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s age and overall health. The primary treatment modalities for thyroid cancer include:a) Surgery: Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for thyroid cancer. The extent of surgery depends on the type and stage of the cancer. Thyroidectomy involves removing part or all of the thyroid gland, along with any affected lymph nodes. In some cases, a modified radical neck dissection may be performed to remove affected lymph nodes in the neck.
b) Radioactive Iodine Therapy: After surgery, radioactive iodine therapy may be recommended to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells. This therapy utilizes radioactive iodine, which is absorbed by thyroid cells and destroys them from within.
c) External Beam Radiation Therapy: In certain cases, external beam radiation therapy may be used to target and destroy cancer cells in the thyroid or surrounding tissues. It is typically employed when the cancer is aggressive or has spread beyond the thyroid.
d) Hormone Replacement Therapy: Since the thyroid gland is involved in hormone production, removal of the gland necessitates hormone replacement therapy to maintain adequate thyroid hormone levels in the body. Synthetic thyroid hormone medications are prescribed to regulate hormone levels.
e) Targeted Therapy: In advanced cases of thyroid cancer, targeted therapy may be used to target specific molecular characteristics of cancer cells and inhibit their growth. These medications are typically used when other treatment options have been ineffective.
- Long-Term Follow-Up and Supportive Care: After treatment, regular follow-up visits are crucial to monitor for recurrence and to manage any potential side effects. Additionally, supportive care measures, such as psychological support, nutritional guidance, and monitoring thyroid hormone levels, are important for the overall well-being of thyroid cancer patients.
Conclusion: Thyroid cancer, although relatively rare, requires careful diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and long-term management. By understanding the different types, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring the available treatment options, individuals can navigate their journey with thyroid cancer more confidently. Regular medical check-ups and open communication with healthcare professionals are vital for achieving optimal outcomes and maintaining a healthy life.