What are the Symptoms of Signs of Skin Cancer ? How to Spot and Treat the Disease
Skin cancer is a prevalent form of cancer that develops in the skin cells. It occurs when the DNA within these cells undergoes genetic mutations, causing them to grow and divide uncontrollably.
Skin cancer is primarily caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds. In this article, we will delve into the details of skin cancer, including its types, causes, methods of detection, and various treatment options available to patients.
- Understanding Skin Cancer: There are three main types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and melanoma. BCC and SCC are the most common types and typically occur in sun-exposed areas of the skin, while melanoma is less common but more aggressive and can spread to other parts of the body. Skin cancer can develop on any part of the body, including areas not exposed to the sun.
- Causes and Risk Factors: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation is the primary cause of skin cancer. Other risk factors include fair skin, a history of sunburns, a family history of skin cancer, a weakened immune system, exposure to certain chemicals, and a large number of moles or atypical moles on the skin. It is important to note that skin cancer can affect people of all skin tones, although individuals with lighter skin are generally at a higher risk.
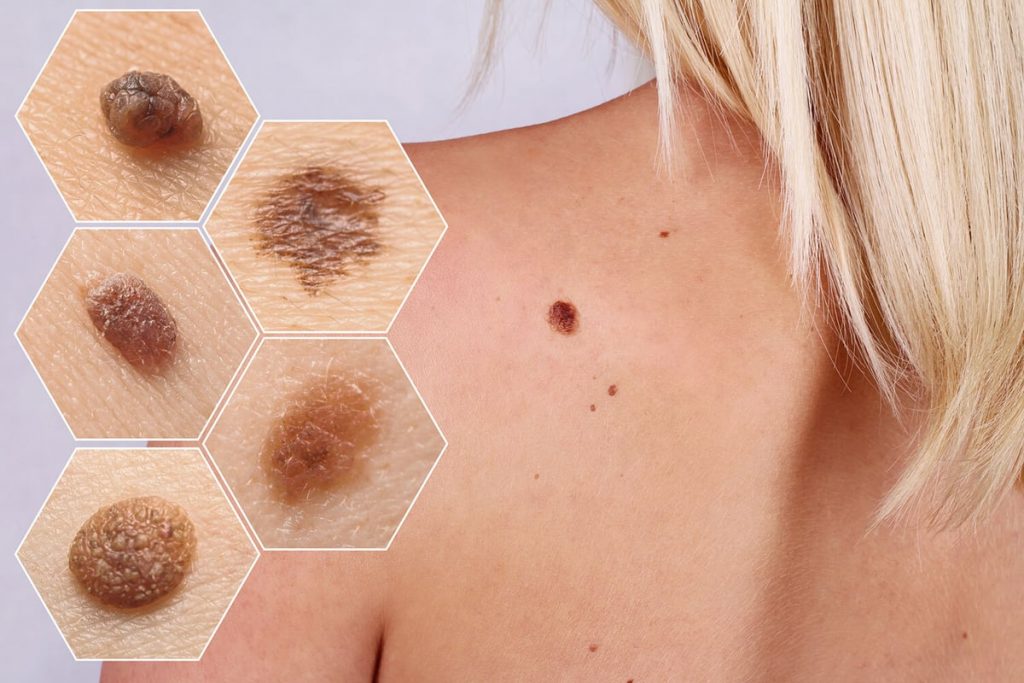
- Symptoms and Detection: Detecting skin cancer early is crucial for successful treatment. Common symptoms and signs include changes in the appearance of moles or birthmarks, the development of new growths or sores that don’t heal, unusual itching, tenderness, or pain in an area of the skin, and changes in the color, shape, or size of existing moles. Regular self-examinations, along with professional skin examinations by dermatologists, can aid in early detection.
- Treatment Options: The choice of treatment for skin cancer depends on various factors, such as the type, stage, location, and size of the tumor, as well as the individual’s overall health. The primary treatment modalities include:a) Surgery: The most common treatment for skin cancer involves surgically removing the cancerous growth and a surrounding margin of healthy tissue. The surgical techniques used may include excision, Mohs surgery (a specialized technique for precise removal), or curettage and electrodesiccation.
b) Radiation Therapy: This treatment option utilizes high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be recommended for certain cases, such as when surgery is not feasible or as an adjuvant therapy to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
c) Topical Medications: For superficial skin cancers or pre-cancerous lesions, topical medications containing substances such as imiquimod, fluorouracil, or ingenol mebutate can be prescribed to destroy or shrink the abnormal cells.
d) Cryotherapy: This procedure involves freezing the cancer cells using liquid nitrogen, causing them to die and eventually slough off.
e) Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy: In advanced cases of skin cancer, targeted therapies or immunotherapies may be recommended to target specific genetic mutations or stimulate the immune system to fight the cancer cells.
- Prevention and Sun Safety: Prevention plays a vital role in reducing the risk of skin cancer. Strategies include wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade during peak sunlight hours, avoiding tanning beds, and regularly examining the skin for any changes.
Conclusion: Skin cancer is a significant health concern, but with early detection and appropriate treatment, the prognosis can be favorable. /albeu.com